Large Language Models for Code Analysis: Do LLMs Really Do Their Job?
- The paper evaluates the effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) in analyzing code, particularly obfuscated code.
- It develops a systematic analysis through a custom dataset and case studies involving real-world code.
- The study highlights both the potential and limitations of LLMs, especially in handling obfuscated code and generating de-obfuscated versions.
Paper Summary (What)
TLDR:
- The paper examines how well large language models (LLMs) can analyze source code and obfuscated code.
- It provides a systematic evaluation using both non-obfuscated and obfuscated datasets.
- The paper tests popular LLMs, including GPT-4, GPT-3.5, LLaMA, and StarChat-Beta, to assess their effectiveness in real-world code analysis scenarios.
Algorithmic Structure:
- The analysis uses transformer-based LLMs like GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and LLaMA, focusing on their ability to analyze and generate code explanations.
- A dataset with a mix of JavaScript, Python, and C code, both obfuscated and non-obfuscated, was used to evaluate model performance.
- The analysis employed both natural language processing techniques (cosine similarity, semantic similarity, etc.) and manual validation by experts to assess the accuracy of the LLM-generated results.
Issues or Targets Addressed by the Paper (Why)
- The primary issue is the lack of a comprehensive evaluation of LLMs’ ability to analyze obfuscated code, a key security-related task in software engineering.
- The paper aims to fill this gap by systematically assessing how well current LLMs understand both regular and obfuscated code, particularly for defensive tasks like malware detection and reverse engineering.
Detailed Information (How)
Problem Setting
- The study involves regression and classification tasks related to code comprehension and code obfuscation.
- LLMs are prompted to analyze both original and obfuscated versions of JavaScript, Python, and C code. The evaluation considers if the LLMs can provide meaningful insights into code functionality and detect security vulnerabilities.
Methodology
- A custom dataset was created with both non-obfuscated and obfuscated code. For obfuscation, JavaScript code was transformed using tools like JavaScript Obfuscator and Wobfuscator.
- The LLMs were tested on their ability to explain and de-obfuscate code, using prompts that mimicked real-world usage, like analyzing snippets of malware and benign programs.
- Manual validation was used to ensure the accuracy of generated results, with a focus on whether the LLMs could generate accurate code summaries and detect malicious behaviors.
Assumptions
- LLMs are expected to generalize their natural language capabilities to code analysis, leveraging contextual understanding of code syntax and patterns.
- The study assumes that larger models like GPT-4 are more effective due to their vast training data and advanced architectures.
Prominent Formulas or Structure
- N/A (The paper focuses on empirical analysis rather than theoretical formula development.)
Results
- Non-obfuscated Code: GPT-4 achieved an accuracy of 97.4% in explaining source code, demonstrating strong capabilities in analyzing code, recognizing patterns, and providing correct function summaries.
- Obfuscated Code: GPT-4 outperformed GPT-3.5 in handling obfuscated code, but both struggled with more advanced obfuscation techniques like control flow flattening and WebAssembly insertion.
- De-obfuscation: Both GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 showed limited success in generating de-obfuscated code, with GPT-4 being more cautious and accurate in identifying potential issues but less successful in producing functional code.
Limitations
- LLMs showed significant drops in accuracy when analyzing code with complex obfuscation techniques.
- Models like LLaMA and StarChat-Beta performed poorly in comparison to GPT models, particularly in generating consistent and meaningful code explanations.
- De-obfuscation capabilities were limited, with most models failing to generate compilable code in more complex cases.
Confusing Aspects of the Paper
- Some parts of the analysis, particularly related to how LLMs handle specific obfuscation techniques, could benefit from more detailed examples and clearer explanations of failure cases.
Conclusions
The Author’s Conclusions
- LLMs like GPT-4 can serve as useful tools for code analysis, but their effectiveness drops significantly when handling obfuscated code.
- While LLMs can generate accurate explanations for non-obfuscated code, their ability to de-obfuscate code or fully understand complex obfuscation techniques is limited.
- The study highlights the potential of LLMs but also underscores the need for further optimization, particularly in handling security-sensitive tasks like malware analysis.
Possible Future Work / Improvements
- Fine-tuning LLMs specifically for code analysis, with a focus on handling obfuscated code, could improve their performance.
- Expanding the dataset to include more diverse and complex obfuscation techniques would provide a more rigorous test of LLM capabilities.
- Developing better de-obfuscation models or integrating external tools to assist LLMs in generating functional code from obfuscated inputs could be a valuable area of future research.
Part 1. Title & Authors
Title: Large Language Models for Code Analysis: Do LLMs Really Do Their Job?
Authors: Chongzhou Fang, Ning Miao, Shaurya Srivastav, et al.
Part 2. Abstract
本文探讨了LLMs在自动化代码分析任务方面的潜力,特别关注混淆代码.它使用常规代码和混淆代码的数据集对 LLM 性能进行了系统评估,并展示了这些模型的前景,尽管在某些领域(例如反混淆)仍然存在限制.
Part 3. Introduction
LLM通过 GitHub Copilot 等工具彻底改变了自然语言处理和代码生成等领域。然而,它们在代码分析(尤其是混淆代码)方面的有效性研究较少。 本文通过评估LLM的代码理解和反混淆任务来解决这一差距,其中重点评估LLMs分析输入代码样本的能力,并测试LLMs是否可以用于防御性分析任务。
本文旨在通过系统的分析来回答两个关键的研究问题:
- LLMs是否理解源代码
- LLMs能否理解混淆代码或可读性低的代码
贡献包括:
- 构建了两个数据集,包括来自流行编程语言的代码样本和来自这些语言的混淆样本,用于评估;
- 我们系统地评估了公开可用的最先进的LLMs的性能,包括在我们的数据集上最常用的GPT和LLaMA家族,并展示了我们的发现
- 我们使用LLMs进行案例研究,分析真实世界的恶意软件,以显示LLMs在这些任务中的能力和局限性
Part 4. Conclusion
较大的LLMs,特别是来自GPT系列的LLMs,在代码分析任务中能力较为突出
另一方面,LLaMA家族的较小模型在这些相同的任务中表现出不令人满意的性能。
在分析混淆代码时,GPT系列的LLMs对于解释相关的任务仍然可以产生合理有用的结果,但可能不会提供反混淆代码
Part 5. Related Work
The paper reviews existing literature on LLMs in code generation and analysis, including the use of models like GPT for tasks such as vulnerability detection and code summarization.
Part 6. Models
采用人工验证。
ground truth:
首先验证gpt4,将标记为正确的描述当做基本事实,用于其他的模型之间的比较
Comparison Metrics:
用以下指标评估模型的生成的解释:
- 余弦相似度,作为粗粒度指标
- 基于bert的语义相似度评分
- 基于ChatGPT的评估,用于二分类回答上
Part 7. Experiments&&Result
LLM Selection
- 使用了包括GPT-3.5-turbo、GPT-4、LLaMA-2-13B、Code-LLaMA-2-13B-Instruct和StarChat-Beta作为模型
Prompt构建
- 在实验中通过不同的步骤与选定的LLM进行交互,包括指导LLM分析代码和其他测量过程
构建非混淆代码数据集
选择了三种语言:JavaScript,Python和C
- 不同的语言有不同的基准进行判断
构建混淆代码数据集
在非混淆代码数据集的JavaScript分支上进行混淆。因为JavaScript代码通常对Web用户是可见的,这使得额外的混淆保护成为必要。
- 作者使用了两种JavaScript混淆器
混淆方法:
- Default Obfuscation DE:将标识符名称替换为无意义的随机生成的字符串,简化源代码以降低可读性,将字符串放在单独的数组中等、
- dead code injection DCI:在默认方案的基础上,在源代码中插入随机无关的代码块
- Control flow flattening (CFF):在默认方案的基础上,改变程序的结构,隐藏控制流信息
- Split string,SS:在默认方案的基础上将长字符串拆分为更短的块,以缓解嵌入文本的信息泄露
- Wobfuscator ( WSM ):对提供的代码进行跨语言混淆
结果
Results on Non-Obfuscated Code Dataset
- GPT-4在三种语言上的整体准确率是97.4%表明GPT-4能够从流行的开源软件库中识别代码片段
- LLMs可能泄露在会话期间从训练中获得的记忆信息,但是这在分析代码时可能是有帮助的
- GPT - 4偶尔会做出错误的联想,因为部分代码块在训练记忆中曾出现过
- GPT利用标识符名称中提供的信息来辅助代码分析
- 其他模型的准确率如下,小模型不能准确分析代码结果

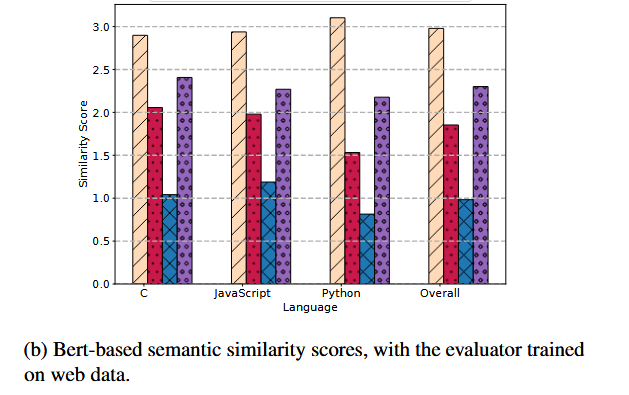

Answer to RQ1:对于非混淆代码,较大的模型(如GPT - 3.5或GPT - 4 )有很高的概率对输入的代码片段产生正确和详细的解释,而较小的模型,即使在代码数据上进行微调,也不能产生正确的输出
Results on Obfuscated Code Dataset
- 衡量方法同非混淆,GPT - 4是始终优于GPT - 3.5
- LLaMA - 2 - 13B、Code - LLaMA - 2 - 13BInstruct和StarChat - Beta在使用混淆技术后无法生成有意义的解释。
- 基本的混淆技术(如DE)对GPT模型执行代码分析的能力影响很小
- LLMs不能破译Wobfuscator生成的混淆代码。
- GPT模型对更长、更复杂的混淆代码的破译能力有限。
- 两个GPT模型去模糊化代码生成能力都不足以应用
- GPT - 4拒绝执行代码生成任务的概率较高,但是生成的代买质量也更高

- 文本层面的混淆并不影响LLM执行反混淆的能力。
Answer to RQ2:
混淆技术会影响LLMs生成解释的能力。较小的模型无法处理混淆代码。GPT - 3.5和GPT - 4在分析精度上都有所下降,尤其是在面对Wobfuscator时,尽管GPT - 4在经典混淆方法上仍然具有可接受的较好的精度。但在没有针对去模糊代码生成进行专门优化的情况下,LLMs生成功能性去模糊代码的能力较差。
Part 8. Discussion & Futher Work
Using LLMs for Code Analysis
- 尽量选用较大的模型
目前捕捉相似性度量的相关方法还不是很可靠,特别是当代码片段和自然语言结合作为输入时,所以构造一个更加精细的metrics是一个潜在的研究方向



